Quick Reference Guide
Here’s everything you need to know about cutter suction dredger cutter ladders at a glance:
| Feature | Pipe-Type Ladder | Box-Type Ladder |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Standard dredging, soft soils | Hard soils, heavy-duty operations |
| Weight | Lighter design | Heavier, more robust |
| Power Range | 50 kW – 5,000 kW | 1,000 kW – 12,000 kW |
| Depth Capability | 15-35 meters | 20-45+ meters |
| Maintenance | Standard intervals | More frequent due to heavy use |
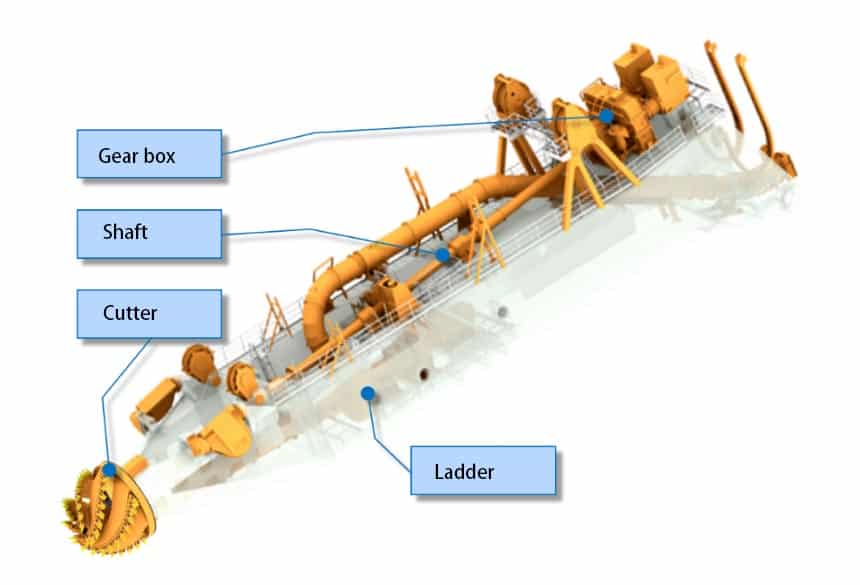
Key Takeaway: The cutter ladder is the backbone of any cutter suction dredger, housing both the rotating cutter head and suction pipe that work together to excavate underwater materials.
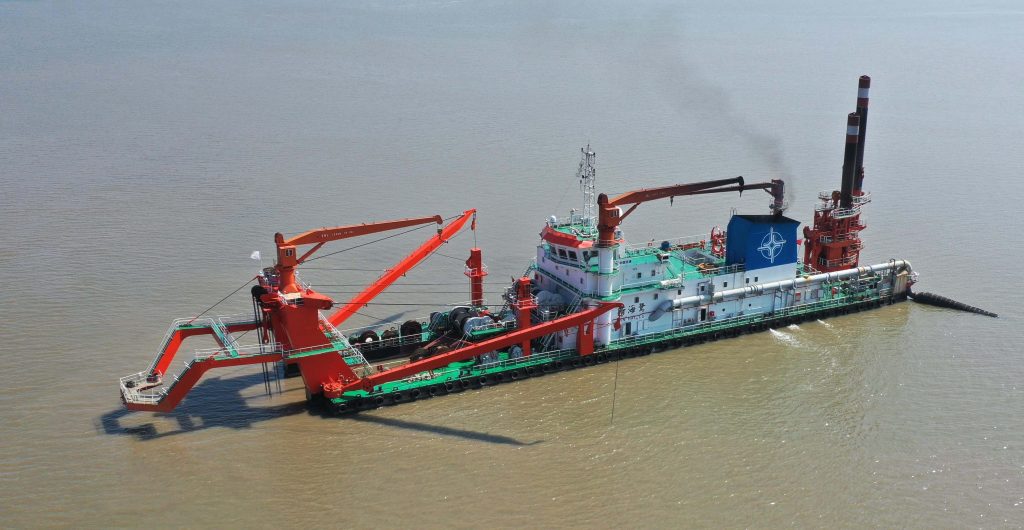
What Is a Cutter Suction Dredger Cutter Ladder?
A cutter suction dredger’s cutter ladder is the mechanical arm that extends from the dredger into the water. Think of it as the “business end” of the entire operation.

The ladder serves three main purposes:
- Houses the cutter head that breaks up sediment and soil
- Contains the suction pipe that transports loosened material
- Provides positioning control for precise excavation depth
Without this crucial component, a cutter suction dredger would be like trying to dig with your bare hands underwater. The ladder makes controlled, efficient excavation possible.
Two Main Types: Pipe-Type vs Box-Type Cutter Ladders
Engineers have developed two distinct ladder designs, each optimized for different conditions:
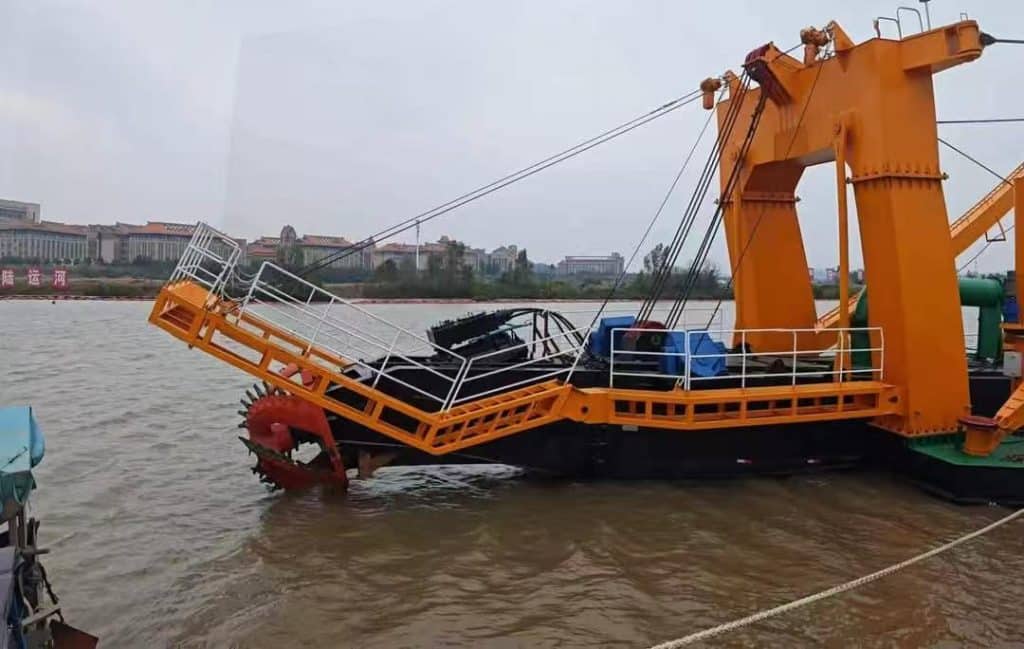
Pipe-Type Cutter Ladders

Pipe-type ladders are the workhorses of standard dredging operations. They feature:
- A streamlined suction line design
- Side wire swivel sheaves for smooth movement
- Lighter overall construction
- Cost-effective manufacturing
These ladders excel in rivers, harbors, and areas with softer sediments. Their simpler design means lower maintenance costs and easier transportation.
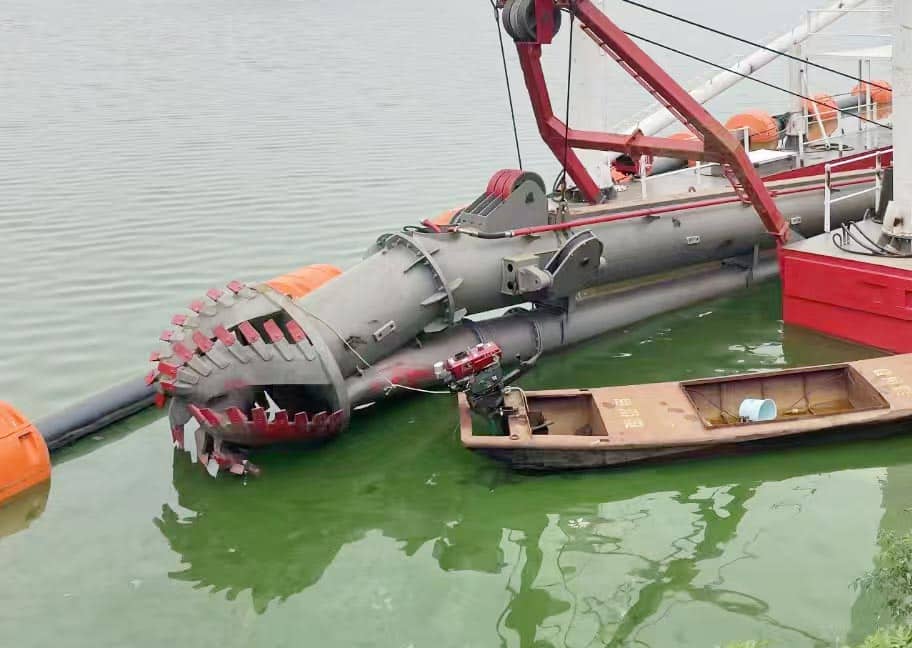
Box-Type Cutter Ladders
When the going gets tough, box-type ladders step up. They offer:
- Reinforced double-box structure
- Internal bracing for stability
- Higher cutter power capacity
- Optional underwater pump integration
These heavy-duty ladders handle rocky seabeds, compacted clay, and other challenging materials that would overwhelm pipe-type designs.
Pro Tip: The choice between pipe-type and box-type ladders often determines the entire dredger’s capabilities. Choose based on your toughest expected conditions, not your average ones.
How Cutter Ladders Work: Step-by-Step Process
Understanding how cutter ladders operate helps explain why they’re so effective:
Step 1: Positioning
The dredger uses spud positioning systems to anchor in place. The ladder then lowers into the water at the desired angle and depth.
Step 2: Cutting Action
The cutter head rotates, using specialized teeth to break up sediment. This loosens material that would otherwise be impossible to suction.
Step 3: Suction and Transport
Simultaneously, the suction system creates powerful vacuum forces. The loosened material flows up through the ladder’s suction pipe.
Step 4: Swing Pattern
The entire ladder swings left and right, creating a systematic excavation pattern. This ensures complete coverage of the target area.
Key Design Components and Features
Modern cutter ladders integrate several sophisticated systems:
Structural Elements
The ladder frame itself consists of:
- Main ladder beam: Provides structural support
- Suction line housing: Protects and guides the suction pipe
- Side wire guides: Enable smooth hoisting and lowering
- Ladder front piece: Houses the cutter head assembly
Cutter Head Integration
The business end of the ladder features either:
- Electric drive systems: Precise control, lower maintenance
- Hydraulic drive systems: Higher torque, better for tough materials
Advanced Features
Cutting-edge ladders now include:
- Dual trunnion systems: Allow depth range from 6.5 to 35 meters
- Quick-switch pipelines: Enable rapid depth changes without manual intervention
- Automated positioning: Reduce operator workload and improve precision
“Advanced dredgers like the Tiankun use dual trunnion bridge ladder systems, dramatically improving operational flexibility across varying depths.”
Performance Specifications That Matter
When evaluating cutter ladders, these specs tell the real story:
Dredging Depth Capabilities
- Standard range: 15-25 meters
- Deep water systems: 35-45 meters
- Specialized units: Up to 60+ meters
Power Ranges
- Small dredgers: 50-500 kW
- Medium dredgers: 500-3,000 kW
- Large dredgers: 3,000-12,000 kW
Production Capacity
- Compact units: 100-500 m³/hour
- Standard units: 500-2,000 m³/hour
- Large units: 2,000-8,000+ m³/hour
These numbers matter because they directly impact project timelines and costs. A properly sized ladder means efficient operations and profitable projects.
Soil Adaptability and Application Guide
Different soil conditions demand different approaches:
Soft Soils (Sand, Silt, Soft Clay)
- Pipe-type ladders work perfectly
- Lower power requirements
- Higher production rates possible
- Minimal cutter tooth wear
Medium Soils (Compacted Sand, Firm Clay)
- Either ladder type works
- Moderate power requirements
- Standard production rates
- Regular cutter teeth maintenance needed
Hard Soils (Rock, Cemented Materials)
- Box-type ladders essential
- High power requirements
- Additional ballast weight needed (up to 880 kN)
- Frequent tooth replacement required
Environmental Applications
Cutter ladders adapt to various environments:
- Rivers and lakes: Excellent performance in calm water
- Harbors and ports: Ideal for maintenance dredging
- Coastal areas: Good performance in moderate waves
- Open sea: Limited by wave conditions
Important Limitation: Cutter suction dredgers struggle in rough seas because waves lift the cutter head off the seabed, reducing efficiency dramatically.
Modern Technology Advances
The dredging industry continues pushing technological boundaries:
Finite Element Analysis
Engineers now use 3D computer modeling to optimize ladder designs. According to the International Journal of Engineering Science, finite element analysis reveals stress points and weak areas before construction, leading to stronger, more efficient ladders.
Energy Efficiency Innovations
Recent advances include:
- LNG power systems: Cleaner burning, reduced emissions
- Waste heat recovery: Captures engine heat for other systems
- Variable frequency drives: Optimize motor efficiency
- Hybrid power systems: Combine diesel and electric power
The International Maritime Organization continues pushing for cleaner marine technologies, driving innovation in dredger power systems.
Automation and Control
Modern ladders feature:
- GPS-guided positioning systems
- Automatic depth control
- Real-time performance monitoring
- Predictive maintenance alerts
These technologies reduce operator fatigue, improve precision, and lower operating costs.
Maintenance and Safety Essentials
Proper maintenance keeps cutter ladders operating safely and efficiently:
Critical Maintenance Points
- Cutter teeth: Inspect daily, replace when worn 50%
- Hydraulic systems: Check fluid levels and pressure weekly
- Wire ropes: Inspect for fraying or broken strands
- Structural welds: Annual inspection for cracks
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration provides comprehensive guidelines for marine equipment maintenance and safety protocols that apply to dredging operations.
Safety Features
Modern ladders include essential safety systems:
- Ladder hoisting wire locks: Prevent accidental dropping
- Tilting pins: Secure ladder during transport
- Emergency stops: Instantly halt all operations
- Load monitoring: Prevent overload damage
Common Wear Factors
Understanding wear patterns helps predict maintenance needs:
- Abrasive soils cause rapid tooth wear
- Rocky conditions stress structural components
- Salt water accelerates corrosion
- High production rates increase overall wear
The integration of dredger pump systems with ladder operations requires coordinated maintenance scheduling for optimal performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the main function of the cutter ladder in a cutter suction dredger?
Q2: What are the differences between pipe-type and box-type cutter ladders?
Q3: How deep can cutter suction dredgers dredge using these ladders?
Q4: What powers the cutter head and ladder systems?
Q5: How does the cutter ladder handle different soil types?
Q6: Can cutter suction dredgers with cutter ladders operate in rough seas?
Q7: What maintenance is required for cutter ladders?
Q8: How long do cutter ladders typically last?
For more detailed information about cutter suction dredger specifications and applications, consulting with experienced manufacturers provides valuable insights for specific project requirements.
Conclusion
Cutter suction dredger cutter ladders are the unsung heroes of underwater excavation. Whether you choose pipe-type for standard jobs or box-type for tough conditions, understanding these systems helps you make smarter dredging decisions.
From riverbeds to ports, these mechanical marvels keep our waterways flowing and our coastlines protected. Next time you see calm water, remember there might be a cutter ladder quietly working beneath the surface.
The right ladder choice makes all the difference between a profitable project and a costly struggle.







