Quick Decision Guide
| Factor | Self Floating Pipes | Floaters |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Long-term operations | Flexible projects |
| Torque Reduction | 60% less than floaters | Standard levels |
| Installation | Simple, no assembly | Requires attachment |
Choosing between self floating dredge pipes and traditional floaters can make or break your dredging project. The wrong choice costs thousands in downtime and repairs.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know. We’ll compare performance data, real-world costs, and practical applications. By the end, you’ll know exactly which system fits your project.
What Are Self-Floating Dredge Pipes?
Self-floating dredge pipes are engineered with built-in buoyancy. Instead of relying on external devices, these pipes integrate flotation directly into their structure.
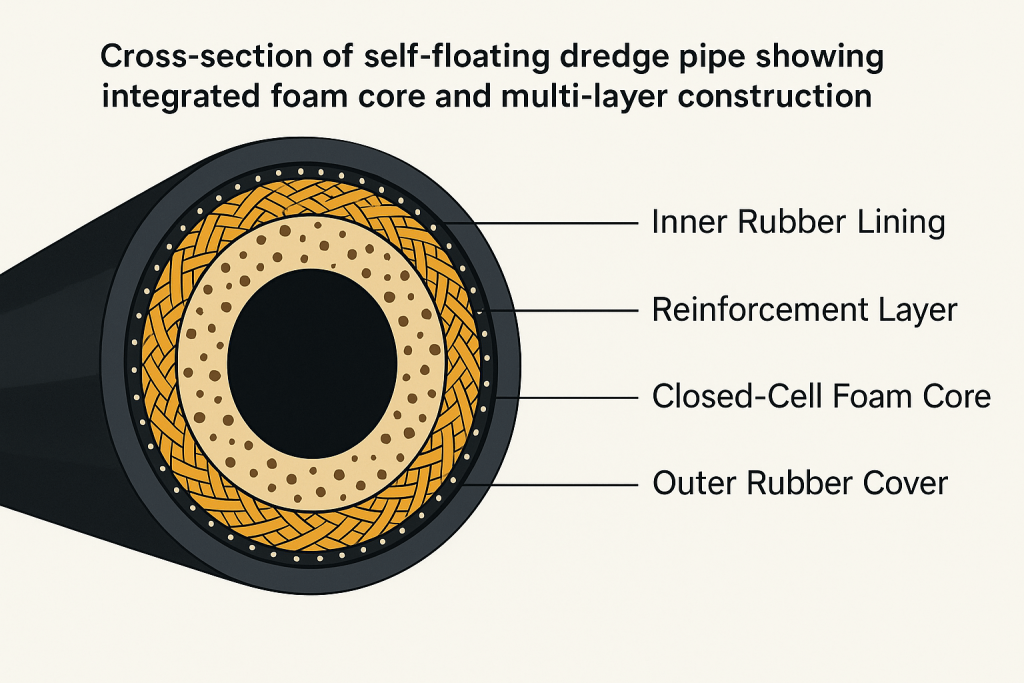
The magic happens in their multi-layered construction. Each pipe contains closed-cell polyethylene foam cores surrounded by high-strength polyester cord reinforcement. The outer layer uses wear-resistant rubber that handles saltwater corrosion and mechanical shock.
Think of it like a life jacket sewn into a coat. The buoyancy becomes part of the pipe itself, not something attached later.
Modern manufacturing uses intelligent coiling machines to control fabric cord winding at precise angles (typically 54°44′). This creates balanced structural integrity that manual assembly can’t match.
Cross-section of self-floating dredge pipe showing integrated foam core and multi-layer construction
These pipes can bend up to 60 degrees without kinking. Their flexibility helps them ride the wave motion instead of fighting it, which makes all the difference in rough seas.
What Are Dredge Pipe Floaters?
Dredge pipe floaters are separate buoyancy devices that attach around standard pipes. Picture pool noodles, but engineered for industrial marine use.
Most floaters use high-density polyethylene (HDPE) shells filled with polyurethane foam. Some premium versions add fiberglass reinforcement for extra durability. The foam filling provides both buoyancy and impact resistance.
Installation involves clamping or bolting floaters around existing pipes at regular intervals. Spacing depends on pipe diameter, wall thickness, and the specific gravity of materials being transported.
The modular design offers flexibility. You can add, remove, or replace individual floaters without affecting the entire pipeline. This adaptability makes floaters popular for projects with changing requirements.
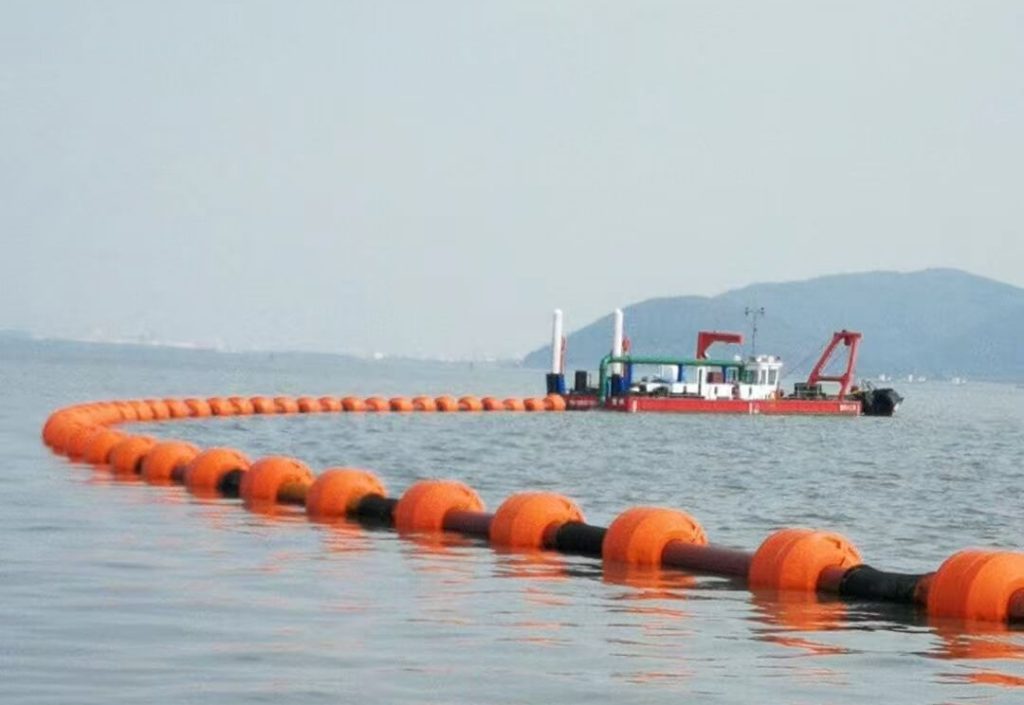

Modular floaters attached to standard dredge pipe showing typical installation pattern
Quality floaters come in bright safety colors with reflective strips. This improves visibility for marine traffic and work crews. Some manufacturers add GPS tracking for asset management.
Key Differences: Self-Floating Pipes vs Floaters
The fundamental difference lies in integration versus modularity. But that simple distinction creates ripple effects across every aspect of operation.
| Feature | Self Floating Pipes | Floaters |
|---|---|---|
| Buoyancy Source | Integrated foam core | External attachment devices |
| Construction | Multi-layer manufacturing | Separate component assembly |
| Installation Time | Immediate deployment | Requires assembly time |
| Maintenance Needs | Minimal, integrated design | Regular floater inspection |
| Adaptability | Fixed configuration | Adjustable and replaceable |
Self floating pipes excel in consistency and simplicity. Once deployed, they perform predictably without ongoing adjustments. Floaters win on flexibility, letting operators modify buoyancy patterns as conditions change.
The choice often comes down to project duration and complexity. Short-term operations favor floaters’ flexibility. Long-term installations benefit from self floating pipes’ reliability.
Performance Comparison in Real Conditions
Real-world performance data reveals significant differences between these systems. Independent testing shows self-floating pipes consistently outperform floater-equipped pipelines in harsh conditions.
Torque and Mooring Forces: Under identical wave, wind, and current conditions, self-floating pipes experience only 60% of the torque compared to floater systems. Even more impressive, mooring forces drop to 50-66% of floater-equipped pipelines.
This translates to real savings. Lower mooring forces mean smaller anchors, shorter installation times, and reduced risk of anchor dragging during storms.
“In 15 years of dredging operations, we’ve never seen torque reduction this dramatic. The integrated design simply handles wave action better than anything we’ve used before.” – Marine Engineering Quarterly
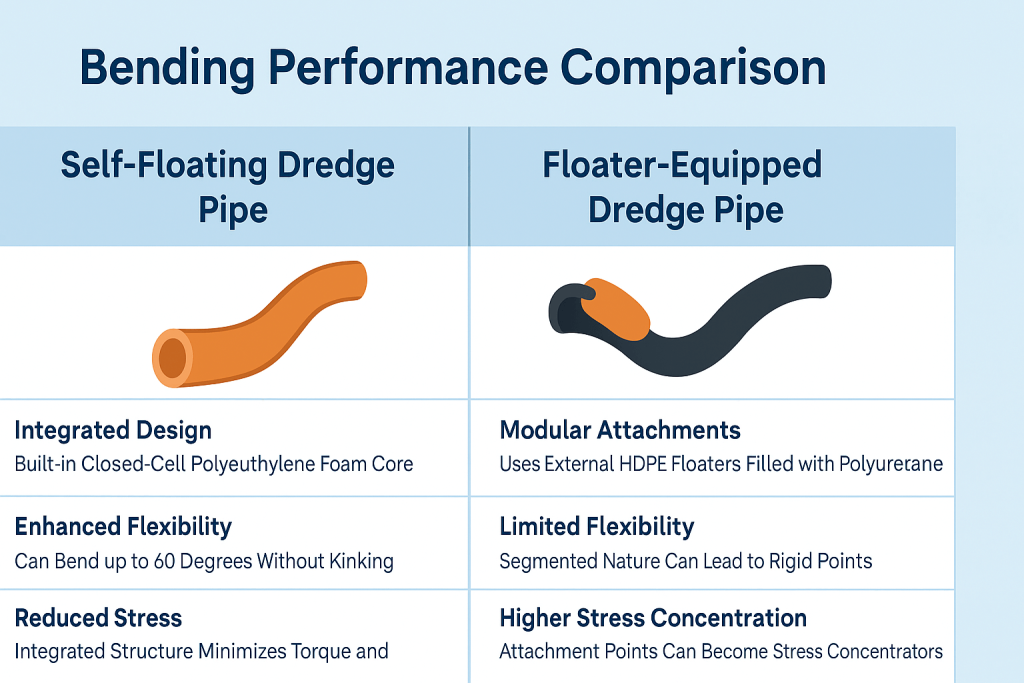
Bending Performance: Self-floating pipes maintain flexibility up to 60 degrees without structural damage. Traditional floater setups often suffer “dead folds” at 90-degree angles, creating weak points that lead to failure.
This flexibility matters during deployment and retrieval. Pipes that can’t bend properly either break or require careful handling, which slows operations.
Bending performance comparison: self-floating pipe (left) vs floater-equipped pipe (right)
Corrosion Resistance: The integrated design of self-floating pipes provides superior protection against seawater corrosion. Multiple sealed layers prevent water infiltration that degrades traditional pipe-floater connections.
According to industry studies, this results in service life extensions of 40-60% compared to conventional systems in marine environments.
Installation and Handling Differences
Installation complexity varies dramatically between these systems. Self-floating pipes arrive ready for immediate deployment. Simply connect sections and launch.
Floater installation requires more steps:
- Diameter matching: Each floater must fit the specific pipe size
- Spacing calculations: Determine optimal floater intervals for proper buoyancy
- Attachment procedures: Secure each floater with clamps or bolts
- Balance verification: Test pipeline stability before full deployment
This process typically adds 2-4 hours per 100 meters of pipeline. For large projects, those hours multiply quickly.
Transportation Considerations: Self-floating pipes ship in compact configurations. The integrated design eliminates separate floater shipping and storage.
Floaters require additional transportation space. A typical project needs 20-30% more shipping volume when floaters are included separately.
However, floaters offer handling advantages during maintenance. Individual components can be removed and replaced without affecting the entire pipeline. This modular approach simplifies repairs in remote locations.
For projects requiring specialized transportation solutions, the compact nature of self-floating pipes often reduces logistical complexity.
Cost Analysis: Initial vs Long-Term
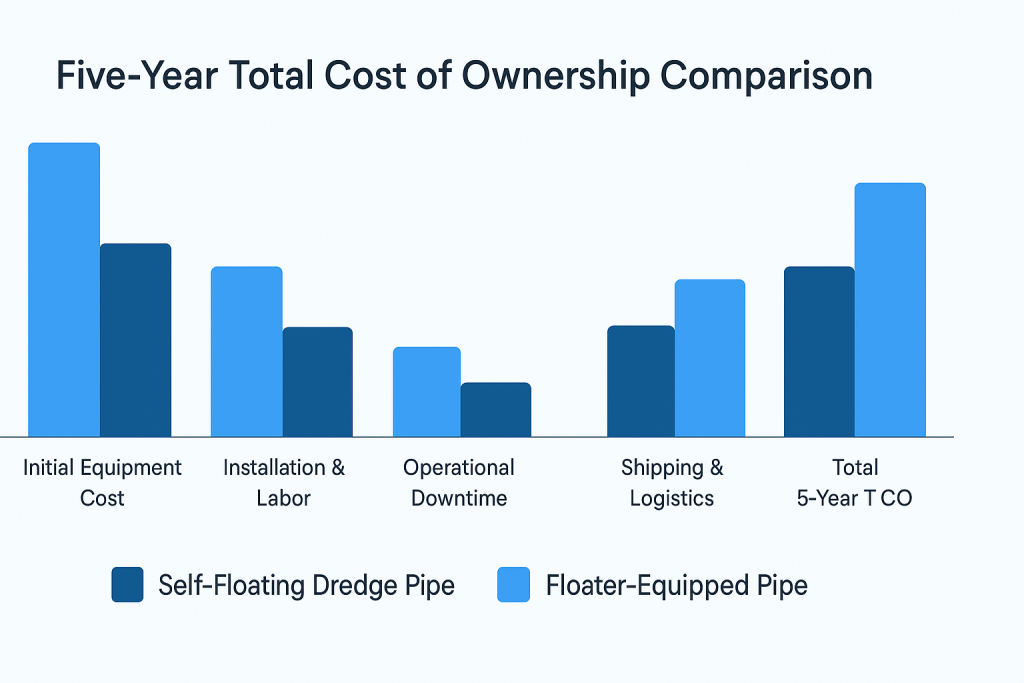
Cost comparison requires looking beyond sticker prices. While self-floating pipes typically cost 15-25% more upfront, total project economics often favor the integrated approach.
Initial Investment Breakdown:
| Cost Factor | Self-Floating Pipes | Standard Pipe + Floaters |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Cost | Higher unit price | Lower combined cost |
| Shipping Volume | Compact shipping | 20-30% more space needed |
| Installation Labor | Minimal assembly time | 2-4 hours per 100m |
Long-Term Economics: Self-floating pipes consume 40% less steel during manufacturing while delivering a longer service life. This efficiency compounds over multi-year projects.
Maintenance costs favor self-floating pipes significantly. The integrated design eliminates floater inspection schedules, replacement parts inventory, and specialized repair procedures.
A recent industry analysis found self-floating systems deliver 20-35% lower total cost of ownership over five-year periods.
Five-year total cost of ownership comparison showing long-term advantages of self-floating systems
Insurance costs may also differ. Some marine insurers offer reduced premiums for self-floating pipe systems due to their lower failure rates and reduced mooring loads.
Which Option Works Best for Different Projects?
Project requirements determine the optimal choice. No single solution works for every situation.
Self-Floating Pipes Excel In:
- Heavy-duty operations: Large-scale mining and port development projects
- Rough water conditions: Exposed coastlines with significant wave action
- Long-term installations: Projects lasting more than 6-12 months
- Remote locations: Areas where maintenance access is limited
- High-pressure applications: Systems requiring consistent structural integrity
Major cutter suction dredging operations particularly benefit from the self-floating pipes’ reliability and reduced mooring requirements.
Floaters Work Better For:
- Flexible projects: Operations with changing scope or duration
- Budget-constrained startups: Projects prioritizing low initial investment
- Calm water environments: Protected harbors and inland waterways
- Equipment sharing: Contractors moving systems between projects
- Partial upgrades: Adding buoyancy to existing pipeline infrastructure
Smaller dredging contractors often prefer floaters’ flexibility when building their equipment inventory gradually.
Environmental Considerations: Both systems address environmental concerns differently. Self-floating pipes minimize pipeline entanglement risks and reduce seabed disturbance. Floaters allow targeted maintenance that reduces waste but require more frequent interventions.
Projects in sensitive marine areas may favor self-floating pipes’ lower environmental impact profile.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between a self-floating dredge pipe and a pipe with floaters?
A: Self-floating pipes have built-in buoyancy through integrated foam cores, while floater systems use external devices attached to standard pipes. Self-floating pipes offer simpler installation and better performance in rough conditions.
Q: Which is more cost-effective: self-floating dredge pipe or using floaters?
A: Self-floating pipes cost more initially but typically deliver 20-35% lower total ownership costs over five years due to reduced maintenance and longer service life. Floaters work better for short-term or budget-limited projects.
Q: How do self-floating dredge pipes work?
A: They integrate closed-cell foam cores within multi-layered construction featuring polyester cord reinforcement and wear-resistant rubber. This creates buoyancy without external components while maintaining structural flexibility.
Q: What materials are used in dredge pipe floaters?
A: Most floaters use high-density polyethylene shells filled with polyurethane foam. Premium versions add fiberglass reinforcement and UV stabilizers for extended marine service life.
Q: Are self-floating dredge pipes better for rough sea conditions?
A: Yes. Testing shows they experience 60% less torque and 50-66% lower mooring forces compared to floater systems. They can bend 60 degrees without damage, while floater systems often suffer dead folds at 90 degrees.
Q: How long do self-floating dredge pipes last compared to pipes with floaters?
A: Self-floating pipes typically last 40-60% longer in marine environments due to superior corrosion resistance and integrated construction. Floaters may need replacement every 3-5 years while the pipes remain serviceable.
Q: Can I convert existing pipes to use floaters?
A: Yes, that’s one of the floaters’ main advantages. They can be retrofitted to most standard HDPE or steel pipes, making them ideal for upgrading existing systems or sharing equipment between projects.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
The choice between self-floating dredge pipes and floaters depends on your specific project requirements, budget constraints, and operational priorities.
Choose self-floating pipes when you need maximum reliability, minimal maintenance, and superior performance in challenging conditions. They’re the smart choice for large-scale, long-term operations where consistent performance matters more than initial cost savings.
Select floaters when flexibility, lower upfront investment, or compatibility with existing equipment drives your decision. They excel in shorter-duration projects or situations requiring frequent system modifications.
Quick Decision Checklist:
- ✓ Project duration over 12 months? Consider self-floating pipes
- ✓ Rough water conditions expected? Self-floating pipes handle waves better
- ✓ Need maximum flexibility? Floaters offer modular advantages
- ✓ Limited initial budget? Floaters cost less upfront
- ✓ Minimal maintenance preferred? Self-floating pipes require less attention
Understanding these trade-offs helps you make an informed decision that aligns with your project goals and constraints. For comprehensive guidance on dredging equipment selection, consider consulting with experienced manufacturers who can provide project-specific recommendations.
Both technologies continue evolving as manufacturers develop new materials and manufacturing techniques. The key is matching the right solution to your specific operational requirements and long-term business objectives.
Conclusion
Self floating dredge pipe and floater systems each serve important roles in modern dredging operations. Self-floating pipes offer superior performance and lower long-term costs for demanding applications, while floaters provide flexibility and affordability for diverse project needs.
Your project’s specific requirements – duration, conditions, budget, and flexibility needs – will determine the optimal choice. Consider both initial costs and long-term operational expenses when making your decision.
The dredging industry continues advancing these technologies. For current market information and technical specifications, consult with industry resources and experienced equipment manufacturers.